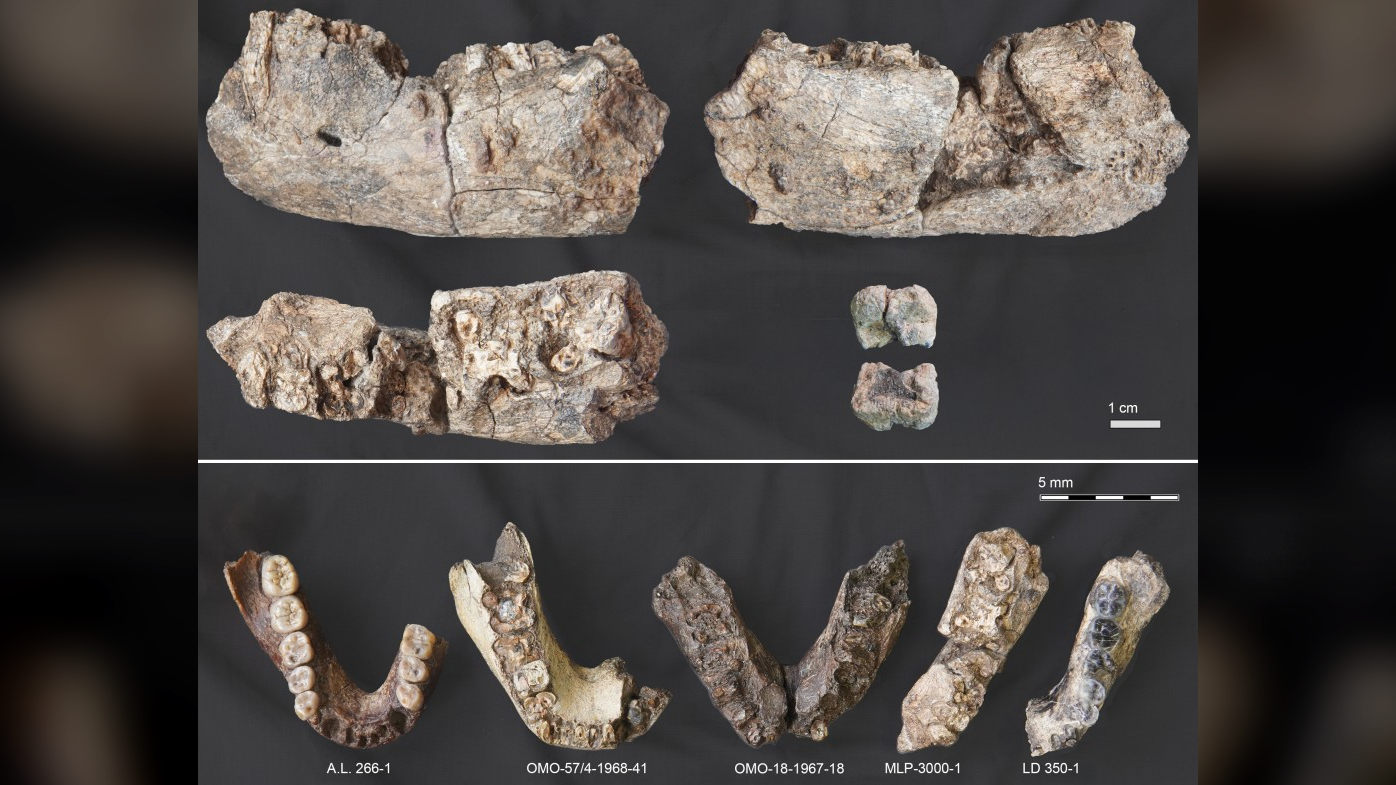
Fragments of a 2.6 million-year-old fossil jaw discovered in northeastern Ethiopia are transforming the picture of early human evolution in Africa. The jaw, from a bipedal hominin — an extinct relative of humans — shows that its kind journeyed far north, to a region where other hominins were already living.
The ancient jaw belongs to the genus Paranthropus and was found more than 620 miles (1,000 kilometers) farther north than any other fossil of its kind.
The genus Paranthropus contains three species distantly related to humans: P. robustus, P. boisei and P. aethiopicus, collectively known as the “robusts.” These species walked upright beginning around 2.7 million years ago, but they are unique in having massive teeth and jaws, which earned one fossil skull the nickname “Nutcracker Man.” Paranthropus fossils were previously found in locations from southern Ethiopia to southern Africa and have been dated to between 2.8 million and 1.4 million years ago.
Jaw-dropping find
In January 2019, paleoanthropologists discovered a partial lower jaw, designated MLP-3000, at the site of Mille-Logya in the Afar region of northeast Ethiopia. Dated to about 2.6 million years ago, the jaw came from an older individual whose teeth and bone structure resembled those of members of the Paranthropus genus. While one species — P. aethiopicus — has been found in southern Ethiopia, the new MLP-3000 jaw was discovered much farther north than any previous fossil from this genus.
“The discovery of Paranthropus in the Afar provides critical new information,” the researchers wrote, suggesting that “the genus could exploit diverse habitats and regions from north Ethiopia to South Africa as Australopithecus and Homo did.” This means that Paranthropus likely had a much more flexible diet than the “Nutcracker Man” moniker suggests, enabling these hominins to disperse and adapt to a wide range of environmental conditions.
The newfound Paranthropus fossil at Mille-Logya adds a third genus to the variety of hominins present in the Afar region between 2.8 million and 2.5 million years ago, including Australopithecus and early Homo. It is not yet clear, though, whether the species would have encountered one another directly.
“Discoveries like this really trigger interesting questions in terms of reviewing, revising, and then coming up with new hypotheses as to what the key differences were between the main hominin groups,” Alemseged said.
Carol Ward, a biological anthropologist at the University of Missouri who was not involved in the study, wrote in an accompanying perspective that, given the diversity of hominin species present, “the revelation that Paranthropus inhabited the Afar between 3 million and 2.4 million years ago is particularly exciting.”
Although all humans on the planet today are one species, hominin diversity lasted millions of years, until our extinct cousins the Neanderthals and Denisovans disappeared more than 30,000 years ago, Ward noted.
“Researchers can no longer accept that humans evolved from a single lineage of species marching towards modernity in isolation from others,” she wrote.