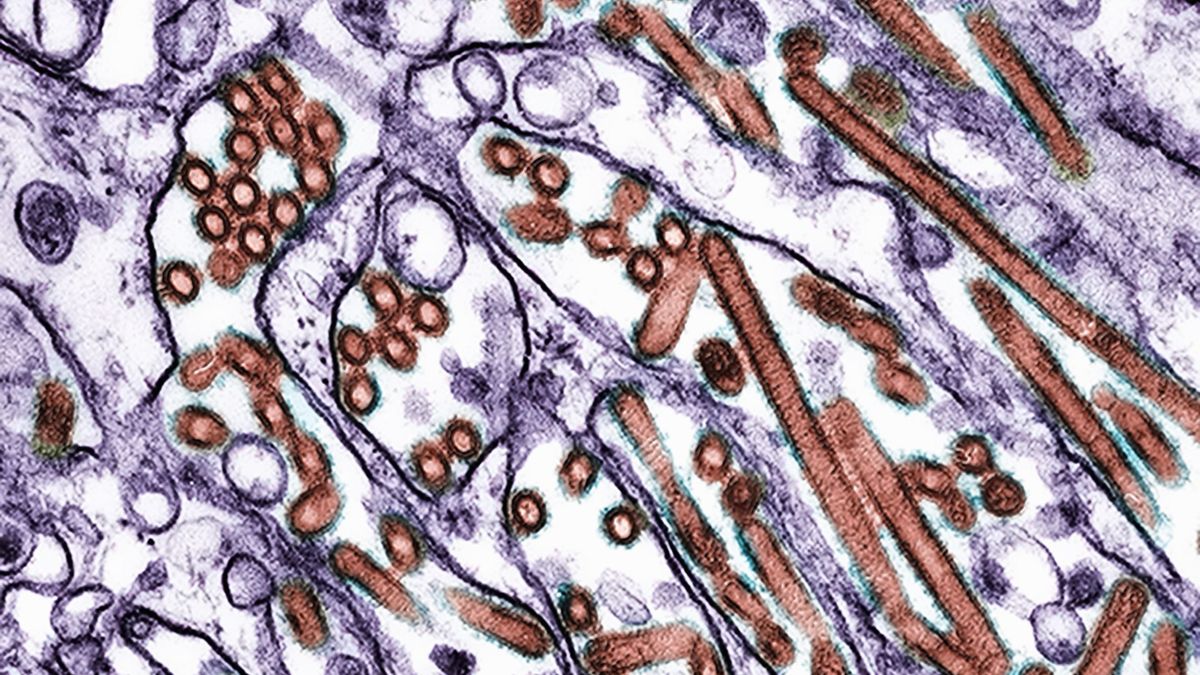
California officials have declared a state of emergency amid growing fears over avian influenza. The virus has swept through dairy herds across the state and caused sporadic cases in humans, with the first severe human bird flu case in the U.S. reported in Louisiana on Wednesday (Dec. 18).
In a statement released Dec. 18, Governor Gavin Newsom’s office said that the action came “as cases were detected in dairy cows on farms in Southern California, signaling the need to further expand monitoring and build on the coordinated statewide approach to contain and mitigate the spread of the virus.”
To date, no person-to-person spread of the virus has been reported in the U.S. and the majority of infected individuals have had known exposure to infected cattle or poultry.
Why has California declared a state of emergency?
The virus H5N1 is a subtype of avian influenza, or bird flu. The virus is spread primarily through wild and domestic birds. However, it can also jump to mammals, such as dairy cows and occasionally humans.
Since the beginning of 2024, a multistate outbreak of the virus has affected 866 dairy herds across the U.S., according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Roughly 75% of these have been in California, largely in the state’s Central Valley.
Related: How to avoid bird flu
Thirty-four of the nation’s 61 confirmed human bird flu cases have also been reported in California, including the first infected child.
Newsom said that the emergency proclamation was a proactive measure to ensure state and local agencies have the resources and flexibility they need to respond rapidly to the outbreak.
“While the risk to the public remains low, we will continue to take all necessary steps to prevent the spread of this virus,” Newsom said in the statement.
What are bird flu symptoms?
With the exception of the patient in Louisiana, the majority of human bird flu infections so far have been mild.
According to the CDC, bird flu may have the following symptoms:
- Eye redness
- Fever
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Muscle and body aches
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
Flu experts have said that it is too early to say whether this could become a more severe outbreak, and flu viruses are constantly changing and mutating. A recent study focused on an H5N1 strain from a cow suggested that a single gene mutation may enable the virus to spread between people, and the infection could become more dangerous if it starts to mix with other seasonal flu viruses. However, the CDC says that the risk to the general public is currently still low.
This article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to offer medical advice.
Ever wonder why some people build muscle more easily than others or why freckles come out in the sun? Send us your questions about how the human body works to [email protected] with the subject line “Health Desk Q,” and you may see your question answered on the website!