Earth’s seasonal cycles can vary dramatically across short distances, even at the same latitudes, a new study suggests.
Researchers have compiled a detailed map of seasonal rhythms around the world, which shows that some physically close regions have dramatically different timing for seasonal variations such as the start and end of the growing season. These differences could contribute to high biodiversity in certain ecosystems, the development of new species and even the different types of coffee harvested in Colombia, the team said.
“Seasonality may often [be] thought of as a simple rhythm — winter, spring, summer, fall — but our work shows that nature’s calendar is far more complex,” study co-author Drew Terasaki Hart, an ecologist and data analyst at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) in Australia, said in a statement. “This is especially true in regions where the shape and timing of the typical local seasonal cycle differs dramatically across the landscape. This can have profound implications for ecology and evolution in these regions.”
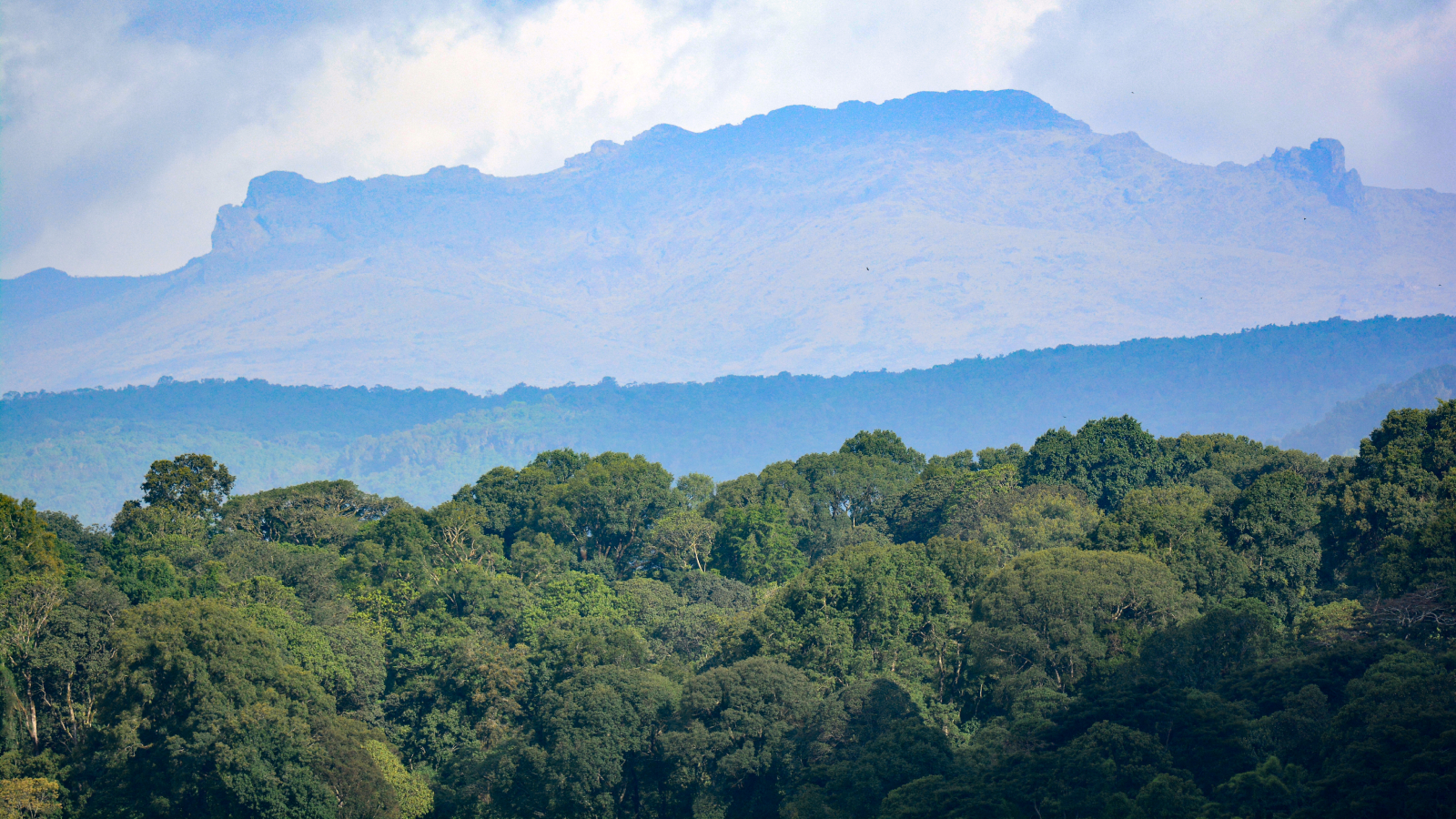
The idea of a simple, seasonal growing pattern works well for plants that grow at high latitudes, such as those in much of Europe and North America, researchers wrote in the study, published Aug. 27 in the journal Nature. But it doesn’t work quite as well in arid or tropical ecosystems.
In the study, Terasaki Hart and his colleagues used 20 years’ worth of satellite data that captured how plants reflected infrared light throughout the year to map vegetation’s growth cycles around the world.
Areas on the slopes of mountains in tropical regions or that have a balmy Mediterranean climate frequently exhibited seasonal asynchrony, or differences in their seasonal cycles across short distances, the team found. In these areas, the availability of light and water was more important for the local plants’ growth cycles than the temperature.
“Our map predicts stark geographic differences in flowering timing and genetic relatedness across a wide variety of plant and animal species,” Terasaki Hart said in the statement. “It even explains the complex geography of coffee harvest seasons in Colombia — a nation where coffee farms separated by a day’s drive over the mountains can have reproductive cycles as out of sync as if they were in opposite hemispheres.”
These starkly different niches over short distances could explain why tropical regions have such high biodiversity, the team wrote in the study. Plant and animal species on different seasonal cycles would slowly diverge, reproducing at different times and possibly forming new species after many years.
The results could help explain how species evolve in other ecosystems, such as in river or ocean environments, as well as how environments are adapting to climate change, the researchers wrote in the study.
“We suggest exciting future directions for evolutionary biology, climate change ecology, and biodiversity research, but this way of looking at the world has interesting implications even further afield, such as in agricultural sciences or epidemiology,” Terasaki Hart added.