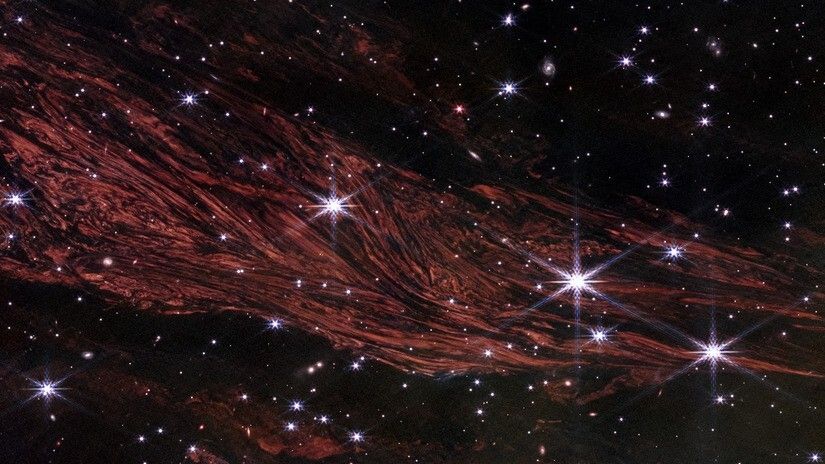
What it is: Interstellar medium near the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A
Where it is: About 11,000 light-years away, in the constellation Cassiopeia
When it was shared: Jan. 14, 2025
Why it’s so special: This set of stunning pictures from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) shows glowing interstellar medium — gas and dust that fill up the space between stars — near the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. The light from this supernova is believed to have reached Earth in the 1660s. More than 350 years later, its intense light has exposed intricate layers of glowing material around the long-dead star.
These images reveal a fascinating phenomenon known as a light echo — faint reflections of the light emitted during a supernova explosion. When a star reaches the end of its lifespan and explodes, it emits intense radiation that lights up the surrounding gas and dust, producing an “echo” that can be seen in visible wavelengths. Sometimes the energetic supernova radiation also warms the nearby gas and dust of the interstellar medium, causing it to emit its own glow, resulting in a rare type of light echo observed at infrared wavelengths — the kind of light that JWST excels at spotting. According to NASA, the infrared light echo in these images actually comes from the material behind Cassiopeia A, not from the material expelled during the explosion.
Related: 42 jaw-dropping James Webb Space Telescope images
The images showcase the tightly packed, sheet-like nature of the interstellar medium, looking a bit like layers of an onion. These filamentary structures were observed in unprecedented detail, with measurements taken on scales of approximately 400 astronomical units (AU), which is 400 times the average distance between Earth and the sun. Previously, astronomers have identified structures in the interstellar medium on scales of parsecs (1 parsec is roughly 206,000 AU, or 3.2 light-years). Discovering that these structures exist on much smaller scales was new to the researchers.
These glittering curtains come from observations of the same patch of dust taken on three different days — Aug. 19, Sept. 16, and Sept. 30, 2024 — using JWST’s Near-Infrared Camera. The three views, once combined, reveal how a light echo changes over time. (In the above images, the field of view in the top row is rotated clockwise just a little bit compared to the middle and bottom rows due to the tilt of the telescope while taking those observations.)
Astronomers plan to further study the scene using JWST’s Mid-Infrared Instrument, hoping to watch the light echo change over weeks or months. This will help them identify changes in the composition of the dust patch and check whether molecules or dust grains get destroyed in the process.